- HIgher exports can generate employment and economic growth
- HIgher exchange rates can cause an increase in the price of exports which would result in a fall in demand in the future
- One country with a high surplus can mean that other countries have deficits (international instability)
Category Archives: Chapter 35: The Balance of Payments Problem
The Current Account
The current account is a record of financial transactions that occur due to international trade while the capital account is a record of any transactions due to savings and investments.
The Current Account :
- Includes both visible and invisible trade as well as income, profits, exports, income paid in the form of interest and imports
- Shows value of imports and exports over a period of time
Current Account Deficit
When balance of trade is greater than the invisible balance, a current account deficit occurs.
A current account deficit may occur because (of):
- Imports may be cheaper than domestically produced goods
- Cost of production may be more expensive as labour costs are high
- There may be low productivity
- A nation may experience an increase in external debt
- Economies of scale
- Inflation
- Inflation reduces the price competitiveness (makes a countries goods and services more expensive)
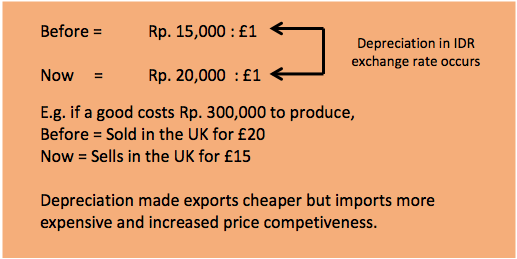
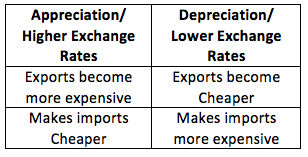
As illustrated by the example above, Depreciation makes exports cheaper and when currency appreciates, exports get more expensive
Fall in IDR helps reduce balance of payments accounts and low exchange rates can cause high unemployment.